OptiLLM-Powered CePO with GPT-OSS-120B: Cerebras Take on Inference Without the Usual Trade-offs
Cerebras has applied CePO, or Cerebras Enhanced Planning and Optimization, to the GPT-OSS-120B model through their inference endpoint. As an OptiLLM technique, CePO leverages test-time computation for iterative planning and refinement, all without retraining the model. CePO works as an inference-time pipeline tailored for Cerebras hardware, allowing the model to plan, iterate on solutions, and refine outputs in real time. As part of the OptiLLM framework, it breaks down complex tasks like code generation into steps: outlining a plan, generating multiple attempts, analyzing for consistency, and picking the strongest result. This uses more tokens overall but turns hardware speed into an advantage for better reasoning, something that is tough on standard setups due to memory limits. The approach builds on earlier work with Llama models and has been extended in updates to models like DeepSeek R1 and Qwen QwQ 32B.
The hardware plays a big role here: Cerebras wafer-scale setup eliminates memory bottlenecks, enabling the iterative fast thinking that CePO relies on. For long contexts, LongCePO improves handling without massive windows.
On LiveCodeBench, a benchmark for code generation from competitive programming problems, GPT-OSS-120B with CePO reaches accuracy levels comparable to closed models like GPT-5, Grok-4 Think, and Claude 4.5 Sonnet. At the same time, it processes queries over three times faster and at about half the cost of those alternatives, based on end-to-end latency and public API pricing. This setup runs on Cerebras wafer-scale hardware, which handles the extra compute needed for these steps efficiently. For those interested in early access to the CePO-enabled GPT-OSS flow, Cerebras is offering a private beta; reach out via their build page. Details come from a recent LinkedIn post by Cerebras leaders Ganesh Venkatesh and Hagay Lupesko, which ties into their NeurIPS 2025 workshop paper on co-designed reasoning.
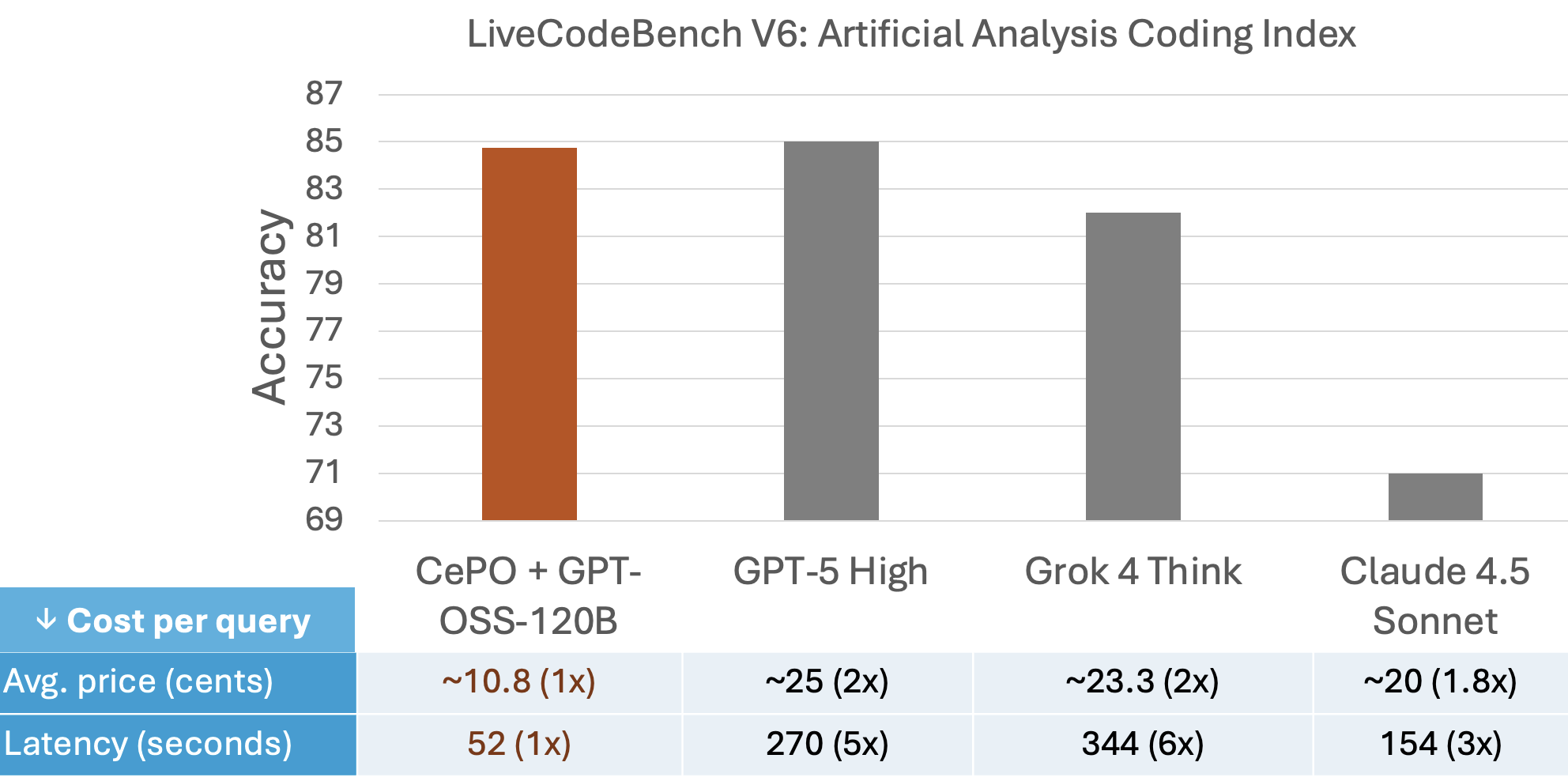
Figure 1: LiveCodeBench performance comparison showing GPT-OSS-120B with CePO against frontier models
On LiveCodeBench (131 problems, early 2025), GPT-OSS-120B with CePO achieves frontier-level code accuracy, matching or slightly edging out GPT-5, Grok-4 Think, and Claude 4.5 Sonnet—as reported by Cerebras. All models were run with high-reasoning settings (≈60k tokens per CePO step for GPT-OSS-120B; up to 128k for GPT-5, similar for others). Under those measured configs and public pricing, end-to-end latency was over 3× faster and cost about 2× lower for the CePO setup.
Looking ahead, early internal experiments on agentic flows with CePO (e.g., on Qwen3 480B) indicate higher coding accuracy with fewer tool calls, while maintaining low latency.
Update: This blog post was updated on November 7, 2025